“Linux Display study”的版本间的差异
来自个人维基
free6d1823(讨论 | 贡献) |
free6d1823(讨论 | 贡献) |
||
| 第9行: | 第9行: | ||
graphic stack alternatives such as Wayland. | graphic stack alternatives such as Wayland. | ||
| − | + | Ap -> [DRM API] -> libDrm -> [ioctls ]-> drm driver | |
| + | libDrm: | ||
| + | vblank event handling, | ||
| + | memory management, | ||
| + | output management, | ||
| + | framebuffer management, | ||
| + | command submission & fencing, | ||
| + | suspend/resume support, | ||
| + | DMA services. | ||
https://blog.csdn.net/yangkuanqaz85988/article/details/48689521 | https://blog.csdn.net/yangkuanqaz85988/article/details/48689521 | ||
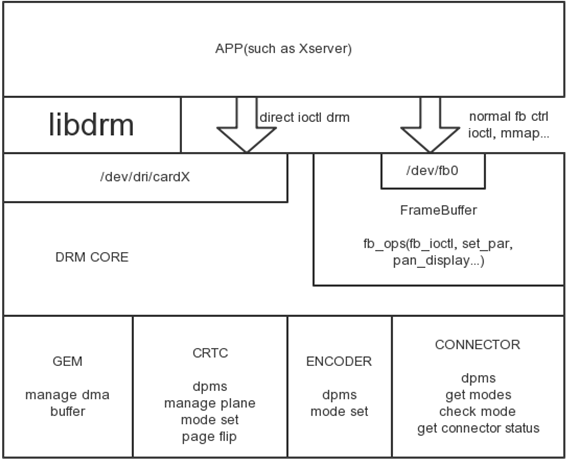
DRM | DRM | ||
[[image:DRM.png]] | [[image:DRM.png]] | ||
2019年11月1日 (五) 11:23的版本
The Direct Rendering Manager (DRM) is a subsystem of the Linux kernel responsible for
interfacing with GPUs of modern video cards. DRM exposes an API that user space programs
can use to send commands and data to the GPU, and perform operations such as configuring
the mode setting of the display. DRM was first developed as the kernel space component of
the X Server's Direct Rendering Infrastructure, but since then it has been used by other
graphic stack alternatives such as Wayland.
Ap -> [DRM API] -> libDrm -> [ioctls ]-> drm driver
libDrm:
vblank event handling, memory management, output management, framebuffer management, command submission & fencing, suspend/resume support, DMA services.
https://blog.csdn.net/yangkuanqaz85988/article/details/48689521
DRM