“Linux Display study”的版本间的差异
free6d1823(讨论 | 贡献) |
free6d1823(讨论 | 贡献) |
||
| 第61行: | 第61行: | ||
//连结handle 代表的物件假的 offset | //连结handle 代表的物件假的 offset | ||
| + | ''Frame Buffer'' | ||
| + | <source lang="c"> | ||
| + | truct drm_framebuffer *(*fb_create)(struct drm_device *dev, | ||
| + | struct drm_file *file_priv, | ||
| + | struct drm_mode_fb_cmd2 *mode_cmd); | ||
| + | int (*create_handle)(struct drm_framebuffer *fb, | ||
| + | struct drm_file *file_priv, unsigned int *handle); | ||
| + | void (*destroy)(struct drm_framebuffer *framebuffer); | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| − | + | ''KMS'' | |
| − | + | ||
https://blog.csdn.net/yangkuanqaz85988/article/details/48689521 | https://blog.csdn.net/yangkuanqaz85988/article/details/48689521 | ||
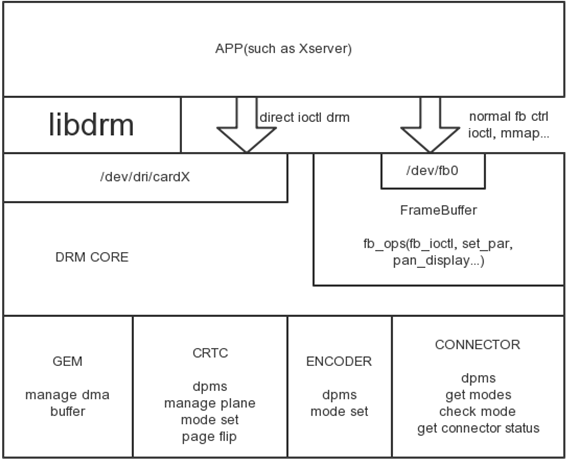
DRM | DRM | ||
[[image:DRM.png]] | [[image:DRM.png]] | ||
2019年11月11日 (一) 11:10的版本
The Direct Rendering Manager (DRM) is a subsystem of the Linux kernel responsible for
interfacing with GPUs of modern video cards. DRM exposes an API that user space programs
can use to send commands and data to the GPU, and perform operations such as configuring
the mode setting of the display. DRM was first developed as the kernel space component of
the X Server's Direct Rendering Infrastructure, but since then it has been used by other
graphic stack alternatives such as Wayland.
Ap -> [DRM API] -> libDrm -> [ioctls ]-> DRM driver
libDrm:
vblank event handling, memory management, output management, framebuffer management, command submission & fencing, suspend/resume support, DMA services.
DRM driver:
drm_driver structure
u32 driver_features; //use AGP,use GEM mem manager, support KMS interfaces, DRM prime buffer sharing, int (*load) (struct drm_device *, unsigned long flags); //driver and device initialization entry point.
Memory management
DRM currently contains two memory managers, the Translation Table Manager (TTM) and the Graphics Execution Manager (GEM).
'GEM'
GEM exposes a set of standard memory-related operations to userspace and a set of helper functions to drivers, and let drivers implement hardware-specific operations with their own private API.
Types of operation:
- Memory allocation and freeing
- Command execution
- Aperture management at command execution time
drm_gem_object_init: will create an shmfs file drm_gem_private_object_init: create GEM objects with no shmfs backing drm_gem_object_alloc: to allocate and initialize a struct drm_gem_object instance, if no need to extend with privae info. drm_gem_object_reference and drm_gem_object_unreference: reference count
communication GEM object between user/kernel space: local handles, global names or,file descriptors.
drm_gem_handle_create: create handle from DRM file and GEM object. drm_gem_handle_delete:
cross process communication use Name.
DRM_IOCTL_GEM_FLINK : handle to name called in user space DRM_IOCTL_GEM_OPEN: name to handle drm_gem_prime_handle_to_fd: Drivers that support GEM file descriptors, also known as the DRM PRIME API drm_gem_prime_fd_to_handle:handle <-> file descriptor.
GEM Objects Mapping: user space mem 的对应, use mmap system API
void *mmap(void *addr, size_t length, int prot, int flags, int fd, off_t offset); (1) driver create GEM object associated with a fake offset. call drm_gem_create_mmap_offset. (2) AP 使用 mmap (offset) 得到 user space address drm_gem_mmap
Dumb GEM Objects
提供简单的标准 创建 GEM 物件的API
dumb_create
dumb_destroy
dumb_map_offset: associates an mmap fake offset with the GEM object given by the handle and returns it.
//连结handle 代表的物件假的 offset
Frame Buffer
truct drm_framebuffer *(*fb_create)(struct drm_device *dev, struct drm_file *file_priv, struct drm_mode_fb_cmd2 *mode_cmd); int (*create_handle)(struct drm_framebuffer *fb, struct drm_file *file_priv, unsigned int *handle); void (*destroy)(struct drm_framebuffer *framebuffer);
KMS
https://blog.csdn.net/yangkuanqaz85988/article/details/48689521
DRM