“PV driver study”的版本间的差异
free6d1823(讨论 | 贡献) |
free6d1823(讨论 | 贡献) |
||
| 第106行: | 第106行: | ||
2. Observe that !(flags & GTF_transfer_committed). [*] | 2. Observe that !(flags & GTF_transfer_committed). [*] | ||
3. Check result of SMP-safe CMPXCHG(&ent->flags, flags, 0). | 3. Check result of SMP-safe CMPXCHG(&ent->flags, flags, 0). | ||
| − | NB. No need for WMB as reuse of entry is control-dependent on success of | + | NB. No need for WMB as reuse of entry is control-dependent on success of step 3, and all architectures guarantee ordering of ctrl-dep writes. |
| − | + | [*] If GTF_transfer_committed is set then the grant entry is 'committed'. The guest must /not/ modify the grant entry until the address of the transferred frame is written. It is safe for the guest to spin waiting for this to occur (detect by observing GTF_transfer_completed in ent->flags). | |
| − | [*] If GTF_transfer_committed is set then the grant entry is 'committed'. | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
- Invalidating a committed GTF_accept_transfer entry: | - Invalidating a committed GTF_accept_transfer entry: | ||
| 第122行: | 第117行: | ||
- Changing a GTF_permit_access from read-only to writable: | - Changing a GTF_permit_access from read-only to writable: | ||
Use SMP-safe bit-setting instruction. | Use SMP-safe bit-setting instruction. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *evtchn Event Channels | ||
| + | the event of interest is signalled by transitioning this bit from 0 to 1. | ||
| + | guests must check the value of the bit after re-enabling event delivery to ensure no missed notifications. | ||
2019年12月3日 (二) 17:02的版本
Reference:
https://wiki.xen.org/wiki/Paravirtualization_(PV)
https://wiki.xen.org/wiki/Xen_VGA_Passthrough
https://wiki.xen.org/wiki/Xen_PCI_Passthrough
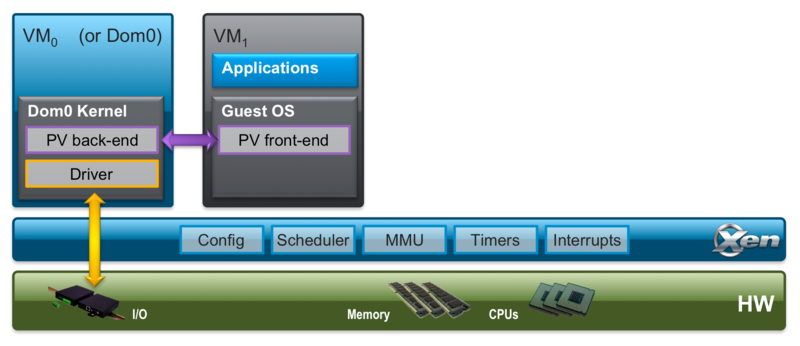
PV support is provided by the paravirt operations extensions (PVOPS) and PV front and back-end drivers that are shipped with Linux.
Xen Project Guest (DomU) support for Linux was introduced into the Linux kernel with version 2.6.24
Xen Project Control Domain (Dom0) support was added from version 2.6.37. The key drivers have been added to Linux v 3.0 and since additional drivers and optimizations are added.
backend driver = driver required in the Xen dom0 kernel
frontend driver = driver required in the Xen domU guest kernel
pciback and pcifront = drivers required for PCI passthrough. These drivers are not related to using PCI devices in dom0!
usbback and usbfront = drivers required for USB passthrough. These drivers are not related to using physical usb devices in dom0!
scsiback and scsifront = drivers required for PVSCSI passthrough. These drivers are not related to using SCSI devices in dom0!
- Xen VGA graphics adapter passthrough
requires IOMMU (Intel VT-d) support from the motherboard chipset, from the motherboard BIOS and from Xen.
VGA 需要bios, 但DomU没有bios, 所以这个需要bios 有虚拟化支持 .
Note that some graphics cards might work in the PV domU just by using the normal Xen PCI passthru.
新的图形卡应该直接看PCI passthru.
- PCI 穿越
Dom0 发现pci device 把它连接给 pciback driver. DomU 由 QEMU 模拟的 PCI bus 上找到 device 把它跟 pcifront river连接.
安全问题: VM buggy驱动可能损害别的系统. 可由VM 攻击其他系统 .
解法:IOMMU - (1)允许Xen限制device 可access 的memory. (2) allows Xen to give the device the same virtualized memory layout that the guest sees.
Dom 0 Load 方法:
(1) Static assignment for built-in xen-pciback: dom0 kernel command line: xen-pciback.hide=(08:00.0)(08.00.1)(device to passthru)
(2) dynamic load: Dom0 console:
modprobe xen-pciback xl pci-assignable-add <domain>:<bus>:<slot>.<function>
Guest configuration: guest kernel command-line
iommu=soft #pvops kernel swiotlb=force #classic Xen kernel
vm create configue file
pci=['80:00.0',<domain>:<bus>:<slot>.<function>,...]
on Dom0 console command line
xl pci-attach <domain-id> <pci device> <guest virtual slot number> xl pci-detach <domain-id> <pci device> <guest virtual slot number>
- Paravirtualised Memory Management
Reference: https://wiki.xen.org/wiki/X86_Paravirtualised_Memory_Management
Direct Paging: VM 直接写 machine address mapping
The Xen paravirtualised MMU model instead requires that the guest be aware of the P2M mapping and be modified such that instead of writing page table entries mapping virtual addresses to the (pseudo-)physical address space it would instead write entries mapping virtual addresses directly to the machine address space by mapping performing the mapping from pseudo physical to machine addresses itself using the P2M as it writes its page tables.
Page Type:
LN Page table page Pages used as a page table at level N. There are separate types for each of the 4 levels on 64-bit and 3 levels on 32-bit PAE guests. Segment descriptor page Pages used as part of the Global or Local Descriptor tables (GDT/LDT). Writeable Page is writable.
long HYPERVISOR_mmu_update() update page table entry (PTE)
long HYPERVISOR_update_va_mapping()
HYPERVISOR_mmuext_op()
The Physical-to-machine (P2M)
machine-to-physical mapping tables (M2P)
Interrupt Descriptor Table: guest 只能看到virtual IDT
Global/Local Descriptor Tables: A Xen guest is not able to access. read-only in the guest.
Virtual Address Space
0x0000000000000000-0x00007fffffffffff
Fully available to guests
0x0000800000000000-0xffff7fffffffffff
Inaccessible (addresses are 48-bit sign extended)
0xffff800000000000-0xffff807fffffffff
Read only to guests.
0xffff808000000000-0xffff87ffffffffff
Reserved for Xen use
0xffff880000000000-0xffffffffffffffff
Fully Available to guests
For 32-bit guests running on a 64-bit hypervisor guests the virtual address space under 4G (which is all such guests can access is:
0x00000000-0xf57fffff
Fully available to guests
0xf5800000-0xffffffff
Read only to guests.
- gnttab Grant Tables
Xen's grant tables provide a generic mechanism to memory sharing between domains.
Each domain has its own grant table.
grant reference is an integer, which indexes into the grant table.
Linux: drivers/xen/grant_table.c
- Introducing a valid entry into the grant table:
1. Write ent->domid.
2. Write ent->frame:
GTF_permit_access: Frame to which access is permitted.
GTF_accept_transfer: Pseudo-phys frame slot being filled by new
frame, or zero if none.
3. Write memory barrier (WMB).
4. Write ent->flags, inc. valid type.
- Invalidating an unused GTF_permit_access entry:
1. flags = ent->flags.
2. Observe that !(flags & (GTF_reading|GTF_writing)).
3. Check result of SMP-safe CMPXCHG(&ent->flags, flags, 0).
NB. No need for WMB as reuse of entry is control-dependent on success of
step 3, and all architectures guarantee ordering of ctrl-dep writes.
- Invalidating an in-use GTF_permit_access entry:
This cannot be done directly. Request assistance from the domain controller which can set a timeout on the use of a grant entry and take necessary action. (NB. This is not yet implemented!).
- Invalidating an unused GTF_accept_transfer entry:
1. flags = ent->flags.
2. Observe that !(flags & GTF_transfer_committed). [*]
3. Check result of SMP-safe CMPXCHG(&ent->flags, flags, 0).
NB. No need for WMB as reuse of entry is control-dependent on success of step 3, and all architectures guarantee ordering of ctrl-dep writes.
[*] If GTF_transfer_committed is set then the grant entry is 'committed'. The guest must /not/ modify the grant entry until the address of the transferred frame is written. It is safe for the guest to spin waiting for this to occur (detect by observing GTF_transfer_completed in ent->flags).
- Invalidating a committed GTF_accept_transfer entry:
1. Wait for (ent->flags & GTF_transfer_completed).
- Changing a GTF_permit_access from writable to read-only:
Use SMP-safe CMPXCHG to set GTF_readonly, while checking !GTF_writing.
- Changing a GTF_permit_access from read-only to writable:
Use SMP-safe bit-setting instruction.
- evtchn Event Channels
the event of interest is signalled by transitioning this bit from 0 to 1.
guests must check the value of the bit after re-enabling event delivery to ensure no missed notifications.