Introduction To EVS
EVS: Exterior/Extended View System
•* EVS is independent of Automotive OS framework. It can be deployed separately for fast rear-view camera or surround view displays in an Android-based IVI system.
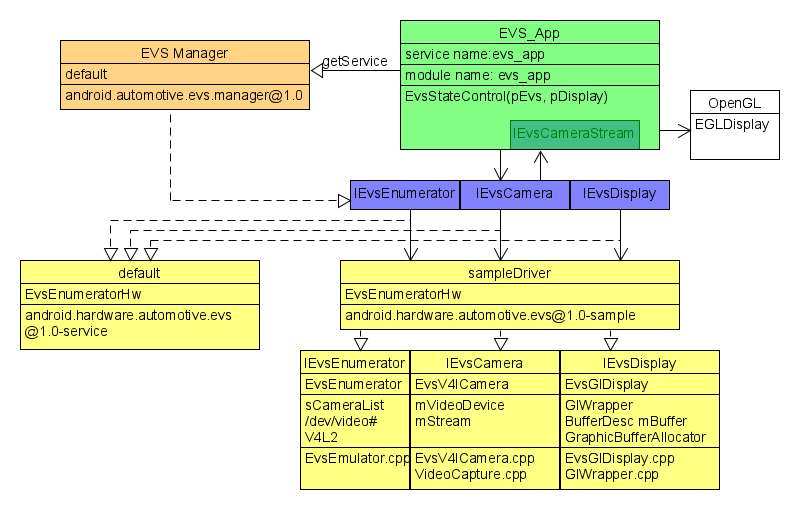
- EVS Manager
| Module name | android.automotive.evs.manager@1.0 |
| Purpose | evs管理器,负责与HAL层的交互,实现HAL层的一些接口,例如openDisplay(),openCamera()等操作。 |
| Register name | default |
| Service name | evs_manager |
| File location | /system/bin/android.automotive.evs.manager@1.0 |
| Source location | /packages/services/Car/evs/manager/ |
- EVS APP
| Module name | evs_app |
| Purpose | evs应用层,负责初始化操作,监听倒车状态,OpenGL 显示, 倒车UI更新等逻辑处理。 |
| Register name | |
| Service name | evs_app |
| File location | /system/bin/evs_app |
| Source location | /packages/services/Car/evs |
- EVS HAL
| Module name | android.hardware.automotive.evs@1.0 |
| Purpose | An automotive HIDL Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) that provides for imagery capture and display very early in the Android boot process and continues functioning for the life of the system |
| Source location | /hardware/interfaces\automotive\evs\1.0 |
EVS HAL 定义四个界面
| IEvsCamera | Represents a single camera and is the primary interface for capturing images. |
| IEvsDisplay | information about the EVS display |
| IEvsEnumerator | Provides the mechanism for EVS camera discovery |
| IEvsCameraStream | Implemented on client side to receive asynchronous video frame deliveries. |
- EVS default driver
| Module name | android.hardware.automotive.evs@1.0-service |
| Purpose | 提供一个模拟倒车测试,显示静态图片模拟倒车;用于测试功能逻辑,不是真实的倒车 |
| Register name | EvsEnumeratorHw |
| Service name | evs-hal-mock |
| File location | /vendor/bin/hw/android.hardware.automotive.evs@1.0-service |
| Source location | /hardware/interfaces/automotive/evs/1.0/default |
- SampleDriver:
| Module name | android.hardware.automotive.evs@1.0-sample |
| Purpose | 驱动层实现,基于v4l2实现的一个驱动Demo程序,供HAL层调用,Camera操作和display操作核心,涉及到摄像头设备操作和display设备操作。 |
| Register name | EvsEnumeratorHw |
| Service name | evs_driver |
| File location | /system/bin/android.hardware.automotive.evs@1.0-sample |
| Source location | /packages/services/Car/evs/sampleDriver |
- Start video flow:
EvsResult EvsV4lCamera::startVideoStream(IEvsCameraStream stream) { mStream = stream; mVideo.startStream(forwardFrame()); ... } bool VideoCapture::startStream( callback) { { memset(&mBufferInfo, 0, sizeof(mBufferInfo)); mBufferInfo.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE; mBufferInfo.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP; mBufferInfo.index = 0; ioctl(mDeviceFd, VIDIOC_QUERYBUF, &mBufferInfo); //向 V4L2 driver询问buffer info 并要求queue 一块capture buffer mPixelBuffer = mmap(NULL, mBufferInfo.length, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, mDeviceFd, mBufferInfo.m.offset); memset(mPixelBuffer, 0, mBufferInfo.length); //Queue the first capture buffer ioctl(mDeviceFd, VIDIOC_QBUF, &mBufferInfo); // Start the video stream int type = mBufferInfo.type; ioctl(mDeviceFd, VIDIOC_STREAMON, &type); mCallback = callback; create_thread( collectFrames()); }
- video capturing loop
void VideoCapture::collectFrames() { while (mRunMode == RUN) { // Wait for a buffer to be ready if (ioctl(mDeviceFd, VIDIOC_DQBUF, &mBufferInfo) < 0) { break; } mFrameReady = true; if (mCallback) { mCallback(&mBufferInfo, mPixelBuffer); } } } // This is the async callback from the video camera that tells us a frame is ready void EvsV4lCamera::forwardFrame(imageBuffer* /*pV4lBuff*/, void* pData) { bool readyForFrame = false; size_t idx = 0; // Identify an available buffer to fill for (idx = 0; idx < mBuffers.size(); idx++) { if (!mBuffers[idx].inUse) { // We're going to make the frame busy mBuffers[idx].inUse = true; mFramesInUse++; readyForFrame = true; } } if (!readyForFrame) { // We need to return the vide buffer so it can capture a new frame mVideo.markFrameConsumed(); } else { // Assemble the buffer description we'll transmit below BufferDesc buff = {}; buff.width = mVideo.getWidth(); buff.height = mVideo.getHeight(); buff.stride = mStride; buff.format = mFormat; buff.usage = mUsage; buff.bufferId = idx; buff.memHandle = mBuffers[idx].handle; // Lock our output buffer for writing void *targetPixels = nullptr; GraphicBufferMapper &mapper = GraphicBufferMapper::get(); mapper.lock(buff.memHandle, GRALLOC_USAGE_SW_WRITE_OFTEN | GRALLOC_USAGE_SW_READ_NEVER, android::Rect(buff.width, buff.height), (void **) &targetPixels); // Transfer the video image into the output buffer, making any needed // format conversion along the way // 把V4L2 buffer 复制到GraphicBuffer 并做格式转换 mFillBufferFromVideo(buff, (uint8_t*)targetPixels, pData, mVideo.getStride()); // Give the video frame back to the underlying device for reuse // Note that we do this before making the client callback to give the underlying // camera more time to capture the next frame. mVideo.markFrameConsumed(); // Issue the (asynchronous) callback to the client -- can't be holding the lock auto result = mStream->deliverFrame(buff); } }
- Discussion
1. Use EVS HAL as virtual camera for remote camera:
Effort: 修改 EvsEmulator 及实现 EvsCamera.
- pro:
Well defined interfaces. Much simpler than Camera3 HAL
Server-Client 架构: Server有root权限操作camera, Client 透过binder 控制界面.
Allow ISV to develope virtual camera application.
- con:
boot time is longer, must wait EvsManager, Driver service, Gralloc service started before EVS_APP start.
EVS API is not so popular. 没有Camera3 的功能: 如 face detection, 3A 调整
Some of the features might not be usefull for our purpose.
Optimization counts on ISV. For example, minimum memcpy.
2. buffer memcpy
IEvsCamera sampleDriver copy V4L2 buffers to GraphicBuffer.
Camera V3.4 CmeraDevice: see also Mali Gralloc Tracing